Mining the Social Web¶
Mining LinkedIn¶
This Jupyter Notebook provides an interactive way to follow along with and explore the examples from the book or video series. The intent behind this notebook is to reinforce the concepts in a fun, convenient, and effective way.
This code has been modified from the original book or video version in order to try to keep pace with developments at LinkedIn. Social media companies continue to modify their APIs and install additional privacy and security measures. Unfortunately, that means it's harder for a casual developer to begin exploring. Some of the code in this chapter requires higher-level permissions in order to run correctly. We have tried to keep the examples as accessible as possible.
LinkedIn API Access¶
LinkedIn implements OAuth 2.0 as one of its standard authentication mechanisms, but still supports OAuth 1.0a, which provides you with four credentials ("API Key", "Secret Key", "OAuth User Token", and "OAuth User Secret") that can be used to gain instant API access with no further fuss or redirections. You can create an app and retrieve these four credentials through the "Developer" section of your account settings as shown below or by navigating directly to https://www.linkedin.com/secure/developer.
Using LinkedIn OAuth credentials to receive an access token suitable for development and accessing your own data¶
import requests
import string
import random
# Remember to first declare and setup a new application on the
# LinkedIn Developer Console: https://www.linkedin.com/developer/apps
# Copy the client ID, secret, and redirect URI in the fields below
CLIENT_ID = ''
CLIENT_SECRET = ''
REDIRECT_URI = 'http://localhost:8888'
# Generate a random string to protect against cross-site request forgery
letters = string.ascii_lowercase
CSRF_TOKEN = ''.join(random.choice(letters) for i in range(24))
# Request authentication URL
auth_params = {'response_type': 'code',
'client_id': CLIENT_ID,
'redirect_uri': REDIRECT_URI,
'state': CSRF_TOKEN,
'scope': 'r_liteprofile,r_emailaddress,w_member_social'}
html = requests.get("https://www.linkedin.com/oauth/v2/authorization",
params = auth_params)
# Print the link to the approval page
print(html.url)
# Click the link below to be taken to your redirect page.
# Inspect the address bar of your browser once you reach your redirect page.
# Copy the code after '&code=...', but don't include '&state=...'
# Then paste it here:
AUTH_CODE =''
ACCESS_TOKEN_URL = 'https://www.linkedin.com/oauth/v2/accessToken'
qd = {'grant_type': 'authorization_code',
'code': AUTH_CODE,
'redirect_uri': REDIRECT_URI,
'client_id': CLIENT_ID,
'client_secret': CLIENT_SECRET}
response = requests.post(ACCESS_TOKEN_URL, data=qd, timeout=60)
response = response.json()
access_token = response['access_token']
print ("Access Token:", access_token)
print ("Expires in (seconds):", response['expires_in'])
Retrieving your LinkedIn profile¶
The LinkedIn API limits which data can be queried, e.g. you can no longer use the API to retrieve your list of connections on LinkedIn.
Read about the changes made to LinkedIn's API in February 2015:
https://developer.linkedin.com/blog/posts/2015/developer-program-changes
# Make HTTP request to retrieve personal profile
import json
params = {'oauth2_access_token': access_token}
response = requests.get('https://api.linkedin.com/v2/me', params = params)
print(json.dumps(response.json(), indent=1))
Displaying specific fields¶
See https://developer.linkedin.com/docs/fields/positions for details on additional field selectors that can be passed in for retrieving additional profile information.
import json
# Make HTTP request to retrieve personal profile
params = {'oauth2_access_token': access_token,
'fields': ["localizedFirstName,localizedLastName,id"]}
response = requests.get('https://api.linkedin.com/v2/me', params = params)
print(json.dumps(response.json(), indent=1))
Using field selector syntax to request additional details for APIs¶
# See https://developer.linkedin.com/docs/fields
# for more information on the field selector syntax
import json
params = {'oauth2_access_token': access_token,
'fields': ['lastName:(preferredLocale:(country,language))']}
response = requests.get('https://api.linkedin.com/v2/me', params = params)
print(json.dumps(response.json(), indent=1))
To get access to more API endpoints, you need to join the LinkedIn Partner Program. We do not cover that here, but for more information visit:
Download your profile data and read in connections data as a CSV file¶
Go download your LinkedIn data here: https://www.linkedin.com/psettings/member-data
Once requested, LinkedIn will prepare an archive of your profile data, which you can then download. Place the contents of the archive in a subfolder, e.g. 'data'.
import os
import csv
# Point this to your 'Connections.csv' file.
CSV_FILE = os.path.join('resources', 'ch04-linkedin', 'Connections.csv')
csvReader = csv.DictReader(open(CSV_FILE), delimiter=',', quotechar='"')
contacts = [row for row in csvReader]
Simple normalization of company suffixes from address book data¶
from prettytable import PrettyTable # pip install prettytable
from collections import Counter
from operator import itemgetter
# Define a set of transforms that converts the first item
# to the second item. Here, we're simply handling some
# commonly known abbreviations, stripping off common suffixes,
# etc.
transforms = [(', Inc.', ''), (', Inc', ''), (', LLC', ''), (', LLP', ''),
(' LLC', ''), (' Inc.', ''), (' Inc', '')]
companies = [c['Company'].strip() for c in contacts if c['Company'].strip() != '']
for i, _ in enumerate(companies):
for transform in transforms:
companies[i] = companies[i].replace(*transform)
pt = PrettyTable(field_names=['Company', 'Freq'])
pt.align = 'l'
c = Counter(companies)
[pt.add_row([company, freq]) for (company, freq) in sorted(c.items(), key=itemgetter(1), reverse=True) if freq > 1]
print(pt)
Standardizing common job titles and computing their frequencies¶
transforms = [
('Sr.', 'Senior'),
('Sr', 'Senior'),
('Jr.', 'Junior'),
('Jr', 'Junior'),
('CEO', 'Chief Executive Officer'),
('COO', 'Chief Operating Officer'),
('CTO', 'Chief Technology Officer'),
('CFO', 'Chief Finance Officer'),
('VP', 'Vice President'),
]
# Read in a list of titles and split apart
# any combined titles like "President/CEO."
# Other variations could be handled as well, such
# as "President & CEO", "President and CEO", etc.
titles = []
for contact in contacts:
titles.extend([t.strip() for t in contact['Position'].split('/')
if contact['Position'].strip() != ''])
# Replace common/known abbreviations
for i, _ in enumerate(titles):
for transform in transforms:
titles[i] = titles[i].replace(*transform)
# Print out a table of titles sorted by frequency
pt = PrettyTable(field_names=['Job Title', 'Freq'])
pt.align = 'l'
c = Counter(titles)
[pt.add_row([title, freq])
for (title, freq) in sorted(c.items(), key=itemgetter(1), reverse=True)
if freq > 1]
print(pt)
# Print out a table of tokens sorted by frequency
tokens = []
for title in titles:
tokens.extend([t.strip(',') for t in title.split()])
pt = PrettyTable(field_names=['Token', 'Freq'])
pt.align = 'l'
c = Counter(tokens)
[pt.add_row([token, freq])
for (token, freq) in sorted(c.items(), key=itemgetter(1), reverse=True)
if freq > 1 and len(token) > 2]
print(pt)
Geocoding locations with Google Maps¶
Visit the Google Developer Console:
https://console.developers.google.com
From there, create an API key and enable the 'Google Maps Geocoding API'. Copy and paste the app key below.
from geopy import geocoders # pip install geopy
GOOGLEMAPS_APP_KEY = ''
g = geocoders.GoogleV3(GOOGLEMAPS_APP_KEY)
location = g.geocode("O'Reilly Media")
print(location)
print('Lat/Lon: {0}, {1}'.format(location.latitude,location.longitude))
print('https://www.google.ca/maps/@{0},{1},17z'.format(location.latitude,location.longitude))
Geocoding locations of LinkedIn connections with Google Maps¶
Since LinkedIn only exports basic contact information, which does not include the contact's location, we can try to infer where they located from the company information. This is not inherently accurate, as many companies have multiple locations, but assuming that the person works at the headquarters, or the company is small as has only one location, then this approach should be at least somewhat accurate.
For example, if someone declares that they work at the University of Toronto, then we can guess that they might also live in Toronto, although it's quite possible that they commute into the city from a nearby town.
for i, c in enumerate(contacts):
progress = '{0:3d} of {1:3d} - '.format(i+1,len(contacts))
company = c['Company']
try:
location = g.geocode(company, exactly_one=True)
except:
print('... Failed to get a location for {0}'.format(company))
location = None
if location != None:
c.update([('Location', location)])
print(progress + company[:50] + ' -- ' + location.address)
else:
c.update([('Location', None)])
print(progress + company[:50] + ' -- ' + 'Unknown Location')
Parsing out states from location results¶
def checkIfUSA(loc):
if loc == None: return False
for comp in loc.raw['address_components']:
if 'country' in comp['types']:
if comp['short_name'] == 'US':
return True
else:
return False
def parseStateFromGoogleMapsLocation(loc):
try:
address_components = loc.raw['address_components']
for comp in address_components:
if 'administrative_area_level_1' in comp['types']:
return comp['short_name']
except:
return None
results = {}
for c in contacts:
loc = c['Location']
if loc == None: continue
if not checkIfUSA(loc): continue
state = parseStateFromGoogleMapsLocation(loc)
if state == None: continue
results.update({loc.address : state})
print(json.dumps(results, indent=1))
Write the data to a JSON file, storing the address, latitude, and longitude data for location¶
CONNECTIONS_DATA = 'linkedin_connections.json'
# Loop over contacts and update the location information to store the
# string address, also adding latitude and longitude information
def serialize_contacts(contacts, output_filename):
for c in contacts:
location = c['Location']
if location != None:
# Convert the location to a string for serialization
c.update([('Location', location.address)])
c.update([('Lat', location.latitude)])
c.update([('Lon', location.longitude)])
f = open(output_filename, 'w')
f.write(json.dumps(contacts, indent=1))
f.close()
return
serialize_contacts(contacts, CONNECTIONS_DATA)
Here's how to power a Cartogram visualization with the data from the "results" variable
from IPython.display import IFrame
from IPython.core.display import display
# Load in a data structure mapping state names to codes.
# e.g. West Virginia is WV
codes = json.loads(open('resources/ch04-linkedin/viz/states-codes.json').read())
from collections import Counter
c = Counter([r[1] for r in results.items()])
states_freqs = { codes[k] : v for (k,v) in c.items() }
# Lace in all of the other states and provide a minimum value for each of them
states_freqs.update({v : 0.2 for v in codes.values() if v not in states_freqs.keys() })
# Write output to file
f = open('resources/ch04-linkedin/viz/states-freqs.json', 'w')
f.write(json.dumps(states_freqs, indent=1))
f.close()
# IPython Notebook can serve files and display them into
# inline frames
display(IFrame(src='resources/ch04-linkedin/viz/cartogram.html', width='100%', height='600px'))
Clustering job titles using a greedy heuristic¶
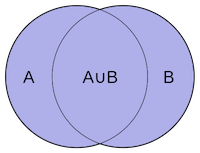
In this section, we introduce the Jaccard distance for comparing two sets of strings. The Jaccard distance is based on the Jaccard Index, which is defined as:
$$ J(A,B) = {{|A \cap B|}\over{|A \cup B|}} = {{|A \cap B|}\over{|A| + |B| - |A \cap B|}} $$The Wikipedia page has a good introduction to the Jaccard Index.

from nltk.util import bigrams
ceo_bigrams = list(bigrams("Chief Executive Officer".split(), pad_left=True, pad_right=True))
cto_bigrams = list(bigrams("Chief Technology Officer".split(), pad_left=True, pad_right=True))
print(ceo_bigrams)
print(cto_bigrams)
print(len(set(ceo_bigrams).intersection(set(cto_bigrams))))
Jaccard distance calculation
from nltk.metrics.distance import jaccard_distance # pip install nltk
job_title_1 = 'Chief Executive Officer'.split()
job_title_2 = 'Chief Technology Officer'.split()
print(job_title_1)
print(job_title_2)
print()
print('Intersection:')
intersection = set(job_title_1).intersection(set(job_title_2))
print(intersection)
print()
print('Union:')
union = set(job_title_1).union(set(job_title_2))
print(union)
print()
print('Similarity:', len(intersection) / len(union))
print('Distance:', jaccard_distance(set(job_title_1), set(job_title_2)))
job_title_1 = 'Vice President, Sales'.split()
job_title_2 = 'Vice President, Customer Relations'.split()
print(job_title_1)
print(job_title_2)
print()
print('Intersection:')
intersection = set(job_title_1).intersection(set(job_title_2))
print(intersection)
print()
print('Union:')
union = set(job_title_1).union(set(job_title_2))
print(union)
print()
print('Similarity:', len(intersection) / len(union))
print('Distance:', jaccard_distance(set(job_title_1), set(job_title_2)))
# Tweak this distance threshold and try different distance calculations
# during experimentation
DISTANCE_THRESHOLD = 0.6
DISTANCE = jaccard_distance
with open(CONNECTIONS_DATA, 'r') as f:
contacts = json.load(f)
def cluster_contacts_by_title():
transforms = [
('Sr.', 'Senior'),
('Sr', 'Senior'),
('Jr.', 'Junior'),
('Jr', 'Junior'),
('CEO', 'Chief Executive Officer'),
('COO', 'Chief Operating Officer'),
('CTO', 'Chief Technology Officer'),
('CFO', 'Chief Finance Officer'),
('VP', 'Vice President'),
]
separators = ['/', ' and ', ' & ', '|', ',']
# Normalize and/or replace known abbreviations
# and build up a list of common titles.
all_titles = []
for i, _ in enumerate(contacts):
if contacts[i]['Position'] == '':
contacts[i]['Position'] = ['']
continue
titles = [contacts[i]['Position']]
all_titles.extend(titles)
all_titles = list(set(all_titles))
clusters = {}
for title1 in all_titles:
clusters[title1] = []
for title2 in all_titles:
if title2 in clusters[title1] or title2 in clusters and title1 \
in clusters[title2]:
continue
try:
distance = DISTANCE(set(title1.split()), set(title2.split()))
except:
print(title1.split())
print(title2.split())
continue
if distance < DISTANCE_THRESHOLD:
clusters[title1].append(title2)
# Flatten out clusters
clusters = [clusters[title] for title in clusters if len(clusters[title]) > 1]
# Round up contacts who are in these clusters and group them together
clustered_contacts = {}
for cluster in clusters:
clustered_contacts[tuple(cluster)] = []
for contact in contacts:
for title in contact['Position']:
if title in cluster:
clustered_contacts[tuple(cluster)].append('{0} {1}.'.format(
contact['FirstName'], contact['LastName'][0]))
return clustered_contacts
clustered_contacts = cluster_contacts_by_title()
for titles in clustered_contacts:
common_titles_heading = 'Common Titles: ' + ', '.join(titles)
descriptive_terms = set(titles[0].split())
for title in titles:
descriptive_terms.intersection_update(set(title.split()))
if len(descriptive_terms) == 0: descriptive_terms = ['***No words in common***']
descriptive_terms_heading = 'Descriptive Terms: ' \
+ ', '.join(descriptive_terms)
print(common_titles_heading)
print('\n'+descriptive_terms_heading)
print('-' * 70)
print('\n'.join(clustered_contacts[titles]))
print()
How to export data to power a dendogram and node-link tree visualization
import nltk
nltk.download('stopwords')
from nltk.metrics.distance import jaccard_distance
from nltk.corpus import stopwords # nltk.download('stopwords')
from cluster import HierarchicalClustering # pip install cluster
CSV_FILE = os.path.join('resources', 'ch04-linkedin', 'Connections.csv')
OUT_FILE = 'resources/ch04-linkedin/viz/d3-data.json'
# Tweak this distance threshold and try different distance calculations
# during experimentation
DISTANCE_THRESHOLD = 0.5
DISTANCE = jaccard_distance
# Adjust sample size as needed to reduce the runtime of the
# nested loop that invokes the DISTANCE function
SAMPLE_SIZE = 500
def cluster_contacts_by_title(csv_file):
csvReader = csv.DictReader(open(csv_file), delimiter=',', quotechar='"')
contacts = [row for row in csvReader]
contacts = contacts[:SAMPLE_SIZE]
transforms = [
('Sr.', 'Senior'),
('Sr', 'Senior'),
('Jr.', 'Junior'),
('Jr', 'Junior'),
('CEO', 'Chief Executive Officer'),
('COO', 'Chief Operating Officer'),
('CTO', 'Chief Technology Officer'),
('CFO', 'Chief Finance Officer'),
('VP', 'Vice President'),
]
separators = ['/', ' and ', '|', ',', ' & ']
# Normalize and/or replace known abbreviations
# and build up a list of common titles.
all_titles = []
for i, _ in enumerate(contacts):
if contacts[i]['Position'] == '':
contacts[i]['Position'] = ['']
continue
titles = [contacts[i]['Position']]
for separator in separators:
for title in titles:
if title.find(separator) >= 0:
titles.remove(title)
titles.extend([title.strip() for title in title.split(separator) if title.strip() != ''])
for transform in transforms:
titles = [title.replace(*transform) for title in titles]
contacts[i]['Position'] = titles
all_titles.extend(titles)
all_titles = list(set(all_titles))
# Define a scoring function
def score(title1, title2):
return DISTANCE(set(title1.split()), set(title2.split()))
# Feed the class your data and the scoring function
hc = HierarchicalClustering(all_titles, score)
# Cluster the data according to a distance threshold
clusters = hc.getlevel(DISTANCE_THRESHOLD)
# Remove singleton clusters
clusters = [c for c in clusters if len(c) > 1]
# Round up contacts who are in these clusters and group them together
clustered_contacts = {}
for cluster in clusters:
clustered_contacts[tuple(cluster)] = []
for contact in contacts:
for title in contact['Position']:
if title in cluster:
clustered_contacts[tuple(cluster)].append('{0} {1}.'.format(
contact['FirstName'], contact['LastName'][0]))
return clustered_contacts, clusters
def get_descriptive_terms(titles):
flatten = lambda l: [item for sublist in l for item in sublist]
title_words = flatten([title.split() for title in titles])
filtered_words = [word for word in title_words \
if word not in stopwords.words('english')]
counter = Counter(filtered_words)
descriptive_terms = counter.most_common(2)
# Get the most common title words from a cluster, ignoring singletons
descriptive_terms = [t[0] for t in descriptive_terms if t[1] > 1]
return descriptive_terms
def display_output(clustered_contacts, clusters):
for title_cluster in clusters:
descriptive_terms = get_descriptive_terms(title_cluster)
common_titles_heading = 'Common Titles: ' + ', '.join((t for t in title_cluster))
descriptive_terms_heading = 'Descriptive Terms: ' + ', '.join((t for t in descriptive_terms))
print(common_titles_heading)
print(descriptive_terms_heading)
print('-' * 70)
#print(title_cluster)
#print(clustered_contacts)
print('\n'.join(clustered_contacts[tuple(title_cluster)]))
print()
def write_d3_json_output(clustered_contacts):
json_output = {'name' : 'My LinkedIn', 'children' : []}
for titles in clustered_contacts:
descriptive_terms = get_descriptive_terms(titles)
json_output['children'].append({'name' : ', '.join(descriptive_terms)[:30],
'children' : [ {'name' : c} for c in clustered_contacts[titles] ] } )
f = open(OUT_FILE, 'w')
f.write(json.dumps(json_output, indent=1))
f.close()
clustered_contacts, clusters = cluster_contacts_by_title(CSV_FILE)
display_output(clustered_contacts, clusters)
write_d3_json_output(clustered_contacts)
Once you've run the code and produced the output for the dendogram and node-link tree visualizations, here's one way to serve it.
from IPython.display import IFrame
from IPython.core.display import display
# Visualize clusters as a dendrogram
viz_file = 'resources/ch04-linkedin/viz/dendogram.html'
display(IFrame(viz_file, '100%', '600px'))
viz_file = 'resources/ch04-linkedin/viz/node_link_tree.html'
# Visualize clusters as a node-link tree
display(IFrame(viz_file, '100%', '600px'))
Clustering your LinkedIn professional network based upon the locations of your connections and emitting KML output for visualization with Google Earth¶
import simplekml # pip install simplekml
from cluster import KMeansClustering
from cluster.util import centroid
# Load this data from where you've previously stored it
CONNECTIONS_DATA = 'linkedin_connections.json'
# Open up your saved connections with extended profile information
# or fetch them again from LinkedIn if you prefer
connections = json.loads(open(CONNECTIONS_DATA).read())
# A KML object for storing all your contacts
kml_all = simplekml.Kml()
for c in connections:
location = c['Location']
if location is not None:
lat, lon = c['Lat'], c['Lon']
kml_all.newpoint(name='{} {}'.format(c['FirstName'],c['LastName']), coords=[(lon,lat)]) # coords reversed
kml_all.save('resources/ch04-linkedin/viz/connections.kml')
# Now cluster your contacts using the K-Means algorithm into K clusters
K = 10
cl = KMeansClustering([(c['Lat'], c['Lon']) for c in connections if c['Location'] is not None])
# Get the centroids for each of the K clusters
centroids = [centroid(c) for c in cl.getclusters(K)]
# A KML object for storing the locations of each of the clusters
kml_clusters = simplekml.Kml()
for i, c in enumerate(centroids):
kml_clusters.newpoint(name='Cluster {}'.format(i), coords=[(c[1],c[0])]) # coords reversed
kml_clusters.save('resources/ch04-linkedin/viz/kmeans_centroids.kml')